The Hidden Dangers of Not Stripping Metadata
When we share a photo, document, or video online, most of us focus on what’s visible. The background, the text, the message. But there’s often something else traveling with that file—something you never meant to share.
That something is metadata.
Metadata is invisible data embedded inside files. And if you don’t strip it before sharing, it can quietly expose far more than you realize.
What Is Metadata, Really?
Metadata is “data about data.” It’s automatically added by devices, apps, and software to help organize files.
Depending on the file type, metadata can include:
-
Exact GPS location (latitude & longitude)
-
Date and time a file was created
-
Device make and model
-
Camera serial number
-
Software used to edit the file
-
Author name, username, or company
-
File revision history
You don’t see this information—but anyone who knows where to look can.
How Metadata Puts You at Risk
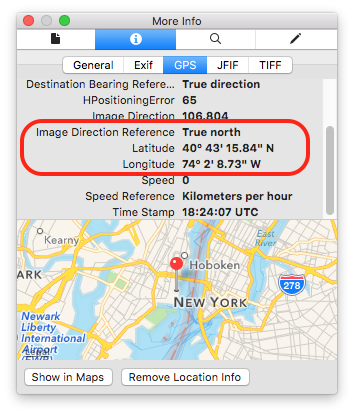
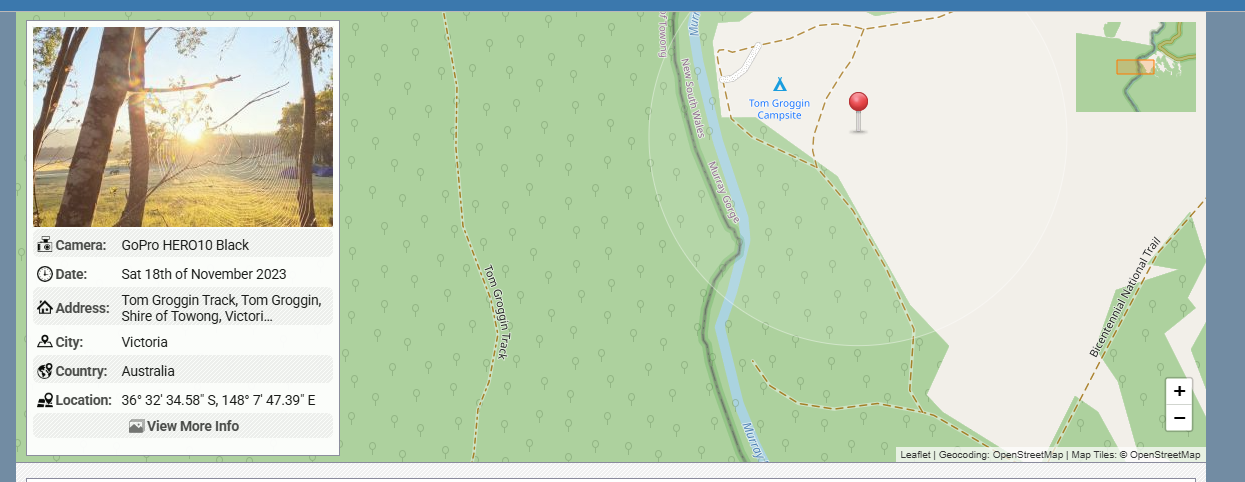
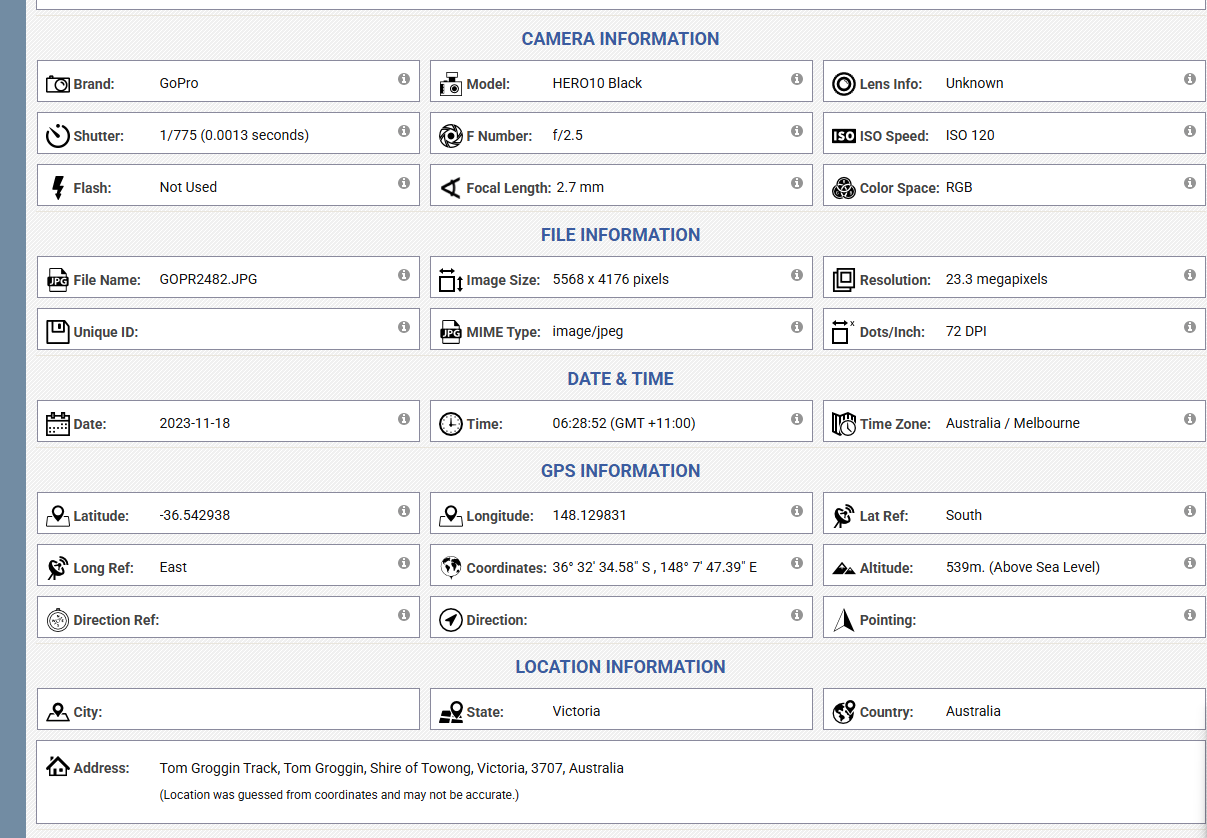
1. Location Tracking Without Consent
Photos taken on smartphones often contain precise GPS coordinates. Sharing a single image can reveal:
-
Your home address
-
Your workplace
-
Your daily routines
-
Locations of children or vulnerable people
For stalkers, criminals, or malicious actors, this is a gift.
2. Doxxing and Identity Exposure
Documents like PDFs, Word files, and spreadsheets may include:
-
Full legal names
-
Internal usernames
-
Company or organization details
-
Editing history showing who touched the file and when
Journalists, activists, whistleblowers, and creators are especially at risk when metadata links anonymous content back to a real identity.
3. Corporate and Operational Leaks
In business environments, metadata can expose:
-
Internal file paths and server names
-
Software versions (useful for exploits)
-
Employee names and roles
-
Project timelines
Attackers use this information for social engineering, phishing, and targeted cyberattacks.
4. Legal and Reputational Consequences
Metadata has been used as evidence in court cases to:
-
Prove when a file was created
-
Show whether an image was altered
-
Identify the original author of a document
Failing to strip metadata can undermine legal claims, violate privacy laws, or break confidentiality agreements.
5. False Sense of Anonymity
Many people believe that removing visible identifiers—like faces, names, or logos—is enough.
It’s not.
Metadata can quietly re-identify you even when the content itself looks anonymous.
Real-World Examples (That Happen More Than You Think)
-
Photos posted online revealing military base locations
-
Anonymous reports traced back to employees via document metadata
-
Influencers unintentionally sharing their home address
-
Journalists exposing sources through unstripped files
These aren’t edge cases. They’re common mistakes.
Why Platforms Can’t Always Protect You
Some platforms strip metadata automatically. Many don’t—or only partially do.
Even when metadata is removed:
-
Original files may still circulate elsewhere
-
Screenshots or re-uploads can preserve data
-
Private sharing (email, cloud links, messaging apps) often keeps metadata intact
The responsibility ultimately falls on the person sharing the file.
How to Protect Yourself
Before sharing any file publicly or privately:
-
Strip metadata from photos and videos
-
Export documents as “clean” PDFs
-
Avoid sharing original files when possible
-
Use tools specifically designed to remove metadata
-
Assume anything you share can be inspected
A few seconds of prevention can save years of damage.
- Tech
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Oyunlar
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness